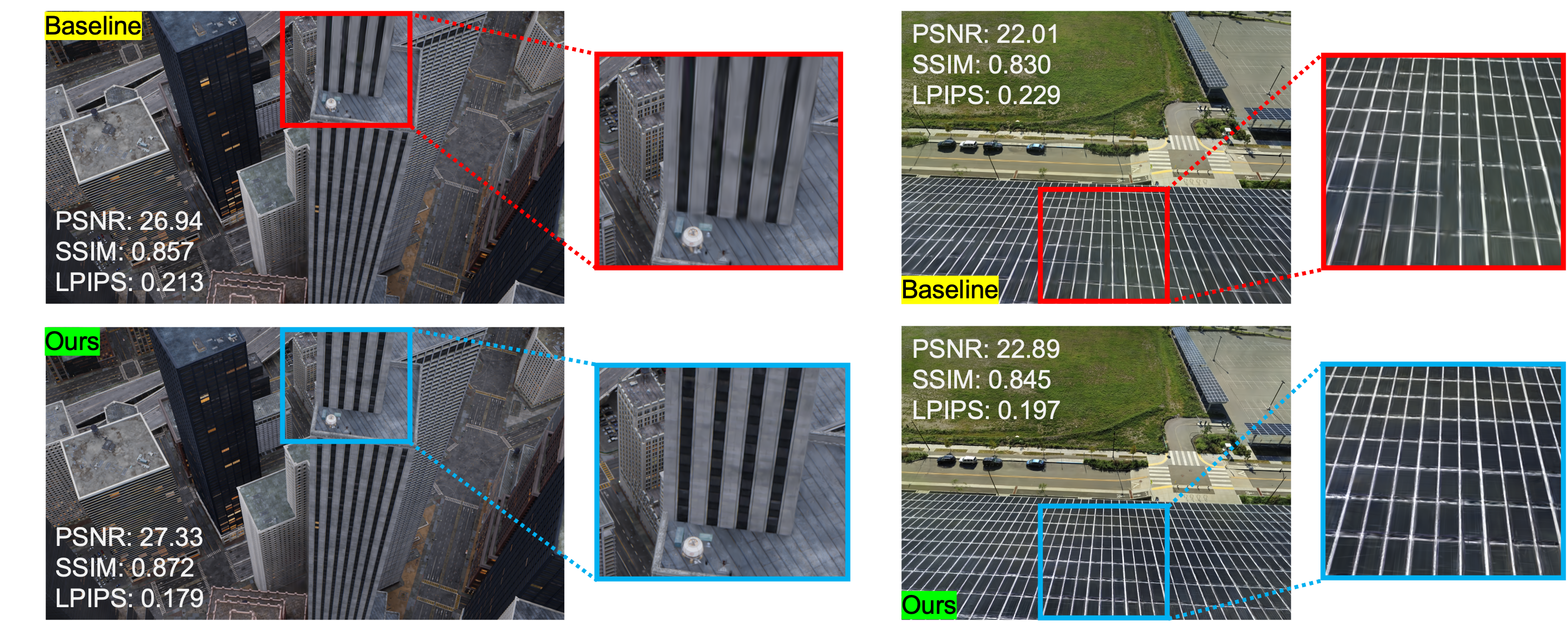
 Fig. 1. Removing noise of 3D Gaussians by adding positional noise.
Fig. 1. Removing noise of 3D Gaussians by adding positional noise.
Abstract
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has proven effective in rapidly rendering 3D spaces by adaptively increasing the density of isotropic Gaussians from initial points. However, the optimization of Gaussian positions remains underexplored. In particular, for larger Gaussians, pixel-wise gradient directions often vary, preventing the Gaussians from converging to appropriate positions. Such unstable Gaussians lead to blurred results in the final rendering, hindering effective reconstruction performance. To address this issue, we propose NoiseGS, a novel method that integrates a noise injection algorithm into the adaptive density control strategy. By introducing random spherical noise to the center positions of Gaussians selected for replication and splitting, NoiseGS provides an opportunity for unstable Gaussians with large gradients to densify into more optimal positions. This approach effectively mitigates the instability caused by large Gaussians and seamlessly integrates with existing heuristic Gaussian optimization techniques. Experimental results demonstrate that NoiseGS achieves remarkable generalization performance across various complex scenes.
Note: This project is being conducted under the supervision of Professor Xuejin Chen from USTC and Professor Jinsun Park from PNU and is currently under review at a double-blind conference.
Qualitative Results
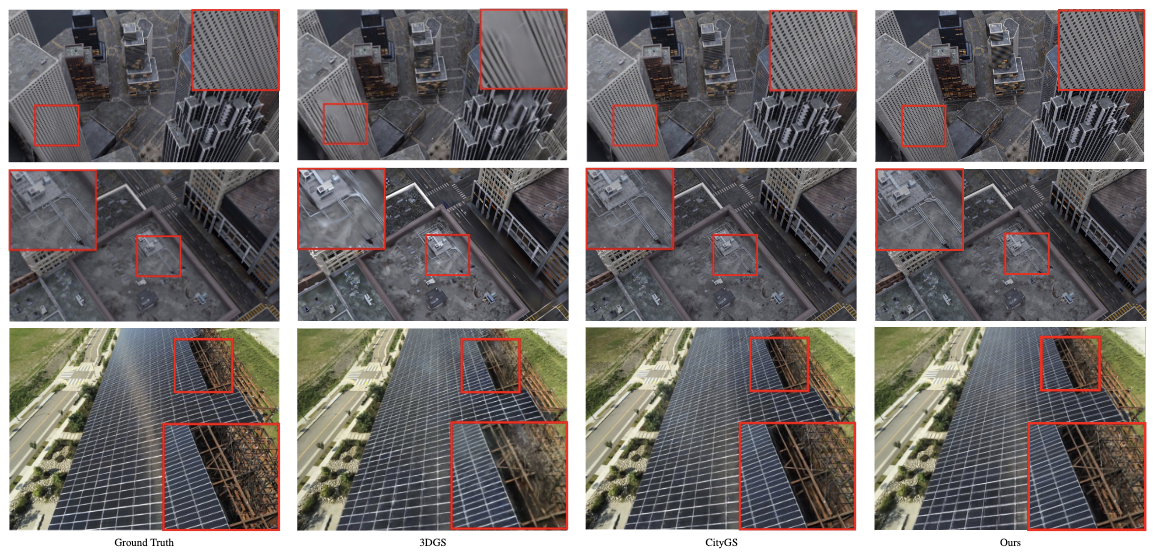
Fig. 2. Qualitative comparison on MatrixCity and Building datasets.
Ablation studies
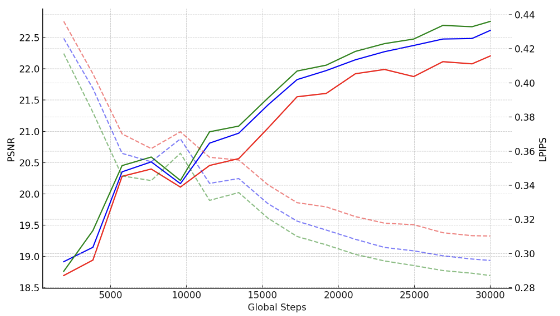
Fig. 3. Ablation study on the Building dataset showing improved performance with + positional noise (blue) and + scale penalization (green)compared to the baseline (red). The solid and dashed lines represent PSNR and LPIPS, respectively.
Citation
Will be updated soon